Information Disclosure Based on TCFD Recommendations Sustainability
Goldwin Group considers the impact of climate change upon our business to be one of our key management issues. Under our long-term vision PLAY EARTH 2030, we are implementing business restructuring aiming to achieve sustainability in terms of both the environment and our business. As part of these efforts, in FY 2022 we declared our support for the Task Force on Climate-related Financial Disclosures (TCFD) recommendations and reorganized our Group initiatives to address climate change. In the future, we will continue to promote full information disclosure based on the recommendations of the Task Force on Climate-Related Financial Disclosures (TCFD), and will respond appropriately to risks such as climate change, with the aim of realizing a sustainable society and to boost our corporate value.

Ⅰ. Governance
We have established the ESG Management Committee, which deliberates on important matters related to sustainability, including climate change. The results of deliberations by the ESG Management Committee are reported to the Board of Directors, which serves as the overseeing body, once a year in light of their degree of importance. The ESG Management Committee is chaired by the President and Representative of Board and creates the basic policy and targets for sustainability including climate change as well as the implementation plans, and reviews progress toward the targets. ESG Management Committee meetings are held quarterly, with participation by company directors, auditors, officers, all employees in positions of general manager and above, and Group company presidents. Based on the basic policy for climate change and priority matters, the Board of Directors creates the business strategy and comprehensively reviews and makes decisions on investment and lending projects. The EMS Committee has been established as the body for implementing improvements to address climate change and other global environmental problems. The committee also advances initiatives for the environment throughout Goldwin Group in collaboration with the GREEN IS GOOD Working Group, a sub-committee of the Development Committee which plays a key role in the Group’s products and technological development.
II. Strategy
We believe that the impacts of climate change pose both risks and opportunities. Our Group is implementing business restructuring aiming to achieve sustainability in terms of both the environment and business under our long-term vision PLAY EARTH 2030. In fiscal 2022, as one aspect of these initiatives, we conducted scenario analysis to evaluate the future impacts of climate change. Under PLAY EARTH 2030, we have established three key environmental issues of “promotion of green design,” referring to a shift to materials with reduced environmental impact, “realization of a carbon-free society,” by promoting carbon neutral at all offices and directly managed stores, and “realization of a circular society,” through zero waste in both products and materials. Regarding the climate change risks and opportunities we considered through our recent scenario analysis, we have confirmed that we will be able to sufficiently address these key environmental issues.
1. Scenario Analysis
(1) Scenario setting
We referenced several internationally recognized climate change scenarios in the analysis of climate-related risks and opportunities. Specially, we referenced the Net Zero Emissions by 2050 Scenario (NZE) released by the International Energy Agency (IEA) in 2021, and Representative Concentration Pathways (RCP 8.5), a greenhouse gas concentration trajectory adopted in the Fifth Assessment Report of the Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change (IPCC) released in 2014, in identifying the risks and opportunities that climate change poses to our Group and for examining our long-term strategy.
| Anticipated world | Reference scenario |
|---|---|
| 1.5℃ (mainly transition risks arise) | IEA : Net Zero Emissions by 2050 Scenario(NZE) |
| 4℃ (mainly physical risks arise) | IPCC : Representative Concentration Pathways (RCP8.5) |
(2) Selection process of main climate-related risk and opportunity factors
We then identified transition and physical risks and opportunities based on the two climate change scenarios of temperature increases of 1.5℃ and 4℃ to inform our examination of business strategy feasibility and our 2030 growth strategy.
Under the 1.5℃ scenario, we consider expected carbon tax and other carbon pricing, and strengthening of environmental regulations as risk factors, and construction of a circular business model, development and deployment of next-generation materials and recycled materials accompanying expansion of the sustainable fashion market as opportunity factors. Also, we believe that changes in consumer trends will be accompanied by the creation of opportunities to enter new markets, such as resale and fashion subscriptions.
Under the 4℃scenario, although these is the possibility that risks and opportunities will not significantly arise by 2030, we consider the occurrence of natural disasters such as typhoons and floods as risk factors that will impact the supply chain. Also, we believe that the increase of such extreme events risks impacting sporting events, while also leading to the creation of new needs.
1.5℃ Scenario
(NZE reference scenario)
Anticipated changes
- Environmental policies and regulations are strengthened, and companies’ greenhouse gas emissions are strictly regulated.
- At the same time, use of renewable energy increases due to enhanced policies to increase its use.
- Consumers are increasingly interested in sustainability, and low-carbon, circular products and services are expanded.
- Disclosure of non-financial information becomes a requirement, and ESG investing becomes established.
- Abnormal weather (frequent typhoons, localized torrential rains, drought, heavy snows, etc.) occurs at about the same frequency as in FY 2022 (current).
Impacts on the apparel industry
- Use of recycled materials and new materials to reduce environmental impacts increases.
- Sustainability is established as new brand value.
- Consumers prefer and select low-carbon, circular products.
- Sustainable fashion influencers appear on the scene.
| Classification | Type of climate change | Category | Risks and opportunities | Main initiatives and countermeasures |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Risks | Transition | Policies and regulations | Higher running costs from introduction of a carbon tax | Initiatives for carbon neutrality (switch to renewable energy, etc.) |
| Higher indirect costs from tightened environmental regulations (calculating GHG emissions, carbon footprint labeling, etc.) | Creating the structure for appropriate reporting and disclosure of greenhouse gas emissions (2025 disclosure target) | |||
| Technology | Increased production costs from switch to materials with reduced environmental impact and recycled materials | Promoting switch to next-generation and recycled materials Cost reductions through industry cooperation and collaboration |
||
| Opportunities | Transition | Increased resource efficiency | Obtaining competitive advantage by building a circular business model | Reducing fashion loss through strengthened order flow. Industry cooperation and collaboration in building a circular business model |
| Products and services | Obtaining a competitive advantage by leading transition to sustainable fashion | Proactive use of materials with reduced environmental impact | ||
| Differentiation through product development using new materials and manufacturing techniques | Launching CVC to discover next-generation materials | |||
| Improving brand image by adapting to changes in customers’ consumption behavior and awareness | Communicating information and launching new products to establish sustainable fashion | |||
| Markets | Capturing new markets by moving into resale, fashion subscriptions, etc. | Examining new businesses including repair services, resale, fashion subscriptions, etc. |
4℃ Scenario
(RCP 8.5 reference scenario)
Anticipated changes
- Strict environmental policies and regulations are deferred, and greenhouse gas emissions increase at the current (FY 2022) rate.
- Some companies introduce renewable energy, but there is strong demand for traditional energy sources.
- ESG investing continues to grow, but use of non-financial information is limited to only some investors.
- The frequency of abnormal weather (frequent typhoons, localized torrential rains, drought, heavy snows, etc.) and extreme weather events increases.
Impacts on the apparel industry
- The supply chain suffers damage from abnormal weather, and production delays are frequent.
- Demand for performance apparel increases as a result of frequent record-breaking extreme weather events, including excessive heat in summer and heavy snows in winter.
| Classification | Type of climate change | Category | Risks and opportunities | Main initiatives and countermeasures |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Risks | Physical | Acute physical risks | Supply chain damage from typhoons, floods and other natural disasters | Strengthened supply chain management |
| Chronic physical risks | Sports events are impacted by the increase in extreme weather events (changes to where events are held, shorter periods when events can be held, fluctuations in competitor populations, etc.) | Focus on trends in competitor populations, reflect trends in production plans and product development | ||
| Opportunities | Transition | Products and services | Meet new needs (both function and fashion) arising from the increase in extreme weather events | Improve performance through use of new materials and manufacturing techniques, and offer Goldwin-centric fashions |
2. Financial Impact Assessment
In our scenario analysis, we verified climate-related factors expected to impact on our Group in the future. In regards to financial impacts, during FY 2022, we conducted calculations limited to a portion of elements, and plan to analyze the details moving forward.
In the future, there is the possibility that expected carbon tax and other carbon pricing will impact our product procurement and store operating costs. We also expect financial impact from the effects of the occurrence of typhoons, floods and other natural disasters upon our supply chain.
We considered increases in the carbon tax rate under the 1.5℃ scenario. Anticipating the introduction of a carbon tax of around 15,000 yen/ t-CO2, we believe the financial impact will be slight, under calculations based on our present GHG emissions (Scope 1, 2). Also, we are promoting the use of recycled materials in product manufacturing, which we concluded will reduce carbon pricing risks. Although we have not conducted quantitative analysis, we believe that the arrival of a society where sustainable fashion is mainstream will provide opportunities, from the perspective of market penetration of advanced environmental initiatives undertaken by our Group.
Regarding the supply chain impact anticipated under a 4℃ scenario, we believe that the financial impacts upon our company will not be serious, forecasting based on the flood damage to sewing factories in Thailand in 2019. We currently consider natural disaster risks when opening new stores, etc., and are engaged in strengthening supply chain management in an effort to minimize the potential for damage. Also, while we anticipate impact on the existing business from the increase in extreme events, we believe that market-trend focused production planning and product development will help us to reduce risks and capture opportunities.
Regarding the risks and opportunities identified through scenario analysis, the long-term vision PLAY EARTH 2030, which our Group is currently advancing, positions initiatives to tackle environmental issues as a key management issue, and we reflect this in our financial strategies. During the five-year period of our medium-term management plan, we plan to generate operating cash flow of 70-80 billion yen. Within this, we plan to invest 15-20 billion yen in new product research and development, 5-10 billion yen in initiatives to reduce environmental burden, and 10-15 billion yen in portfolio reconstruction.
III. Risk Management
We continue our efforts to enhance risk management and corporate governance by establishing various internal committees, such as the ESG Management Committee and Governance Committee, to address risks intrinsic to management issues.
Some of the risks and opportunities associated with climate change are anticipated to arise in the transition to a decarbonized society, and others from the physical impacts of climate change. We classified changes in the external environment associated with climate change, assessed impacts on the apparel industry, and then specified material risks and opportunities for our Group in light of the degree of impact on our Group’s business activities. The specified risks and opportunities are reported to the ESG Management Committee, which sets the action policy, activities and targets as well as reviews the risks and opportunities. Its review is reported to the Board of Directors, which conducts oversight and makes final decisions.
For risks relating to management determinations, including decision-making on management strategy, we consult with law offices and other external experts as necessary, and related departments conduct analysis and investigation.
Ⅳ.Indicators and Targets
1. Indicators and Targets for Assessing Climate-related Risks and Opportunities
In order to adapt to environmental changes in the era of VUCA (volatility, uncertainty, complexity and ambiguity), and to realize sustainable growth, our Group formulated the long-term vision PLAY EARTH 2030, aimed at the coexistence of sustainability in the two dimensions of business and the environment, leveraging our strengths while ascertaining risks and opportunities. Even within this, we established targets with 2030 and 2050 in view, considering initiatives for tackling environmental issues as one of our most important challenges.
We have set medium-term and long-term targets accordingly and are conducting specific activities to achieve environmental improvements, Promoting “green design,” ” realization of a carbon-free society,” and “realization of a circular society” as key environmental issues for improving the global environment.
As part of our promotion of green design, specifically, we aim to use of materials with reduced environmental impact in 100% of our products by FY 2050 through development of Brewed Protein™, switching to use of recycled materials and auxiliary materials with reduced environmental impact. Regarding realization of a carbon-free society, we are converting to use of renewable energy and aim to achieve carbon neutrality including in the supply chain in FY 2050 through enhanced supply chain management. Our plan for realizing a circular society targets zero fashion loss and includes driving total volume control through strengthened order flow and greater industry cooperation for zero fashion loss, and aims to achieve zero waste, including in the supply chain, by FY 2050.
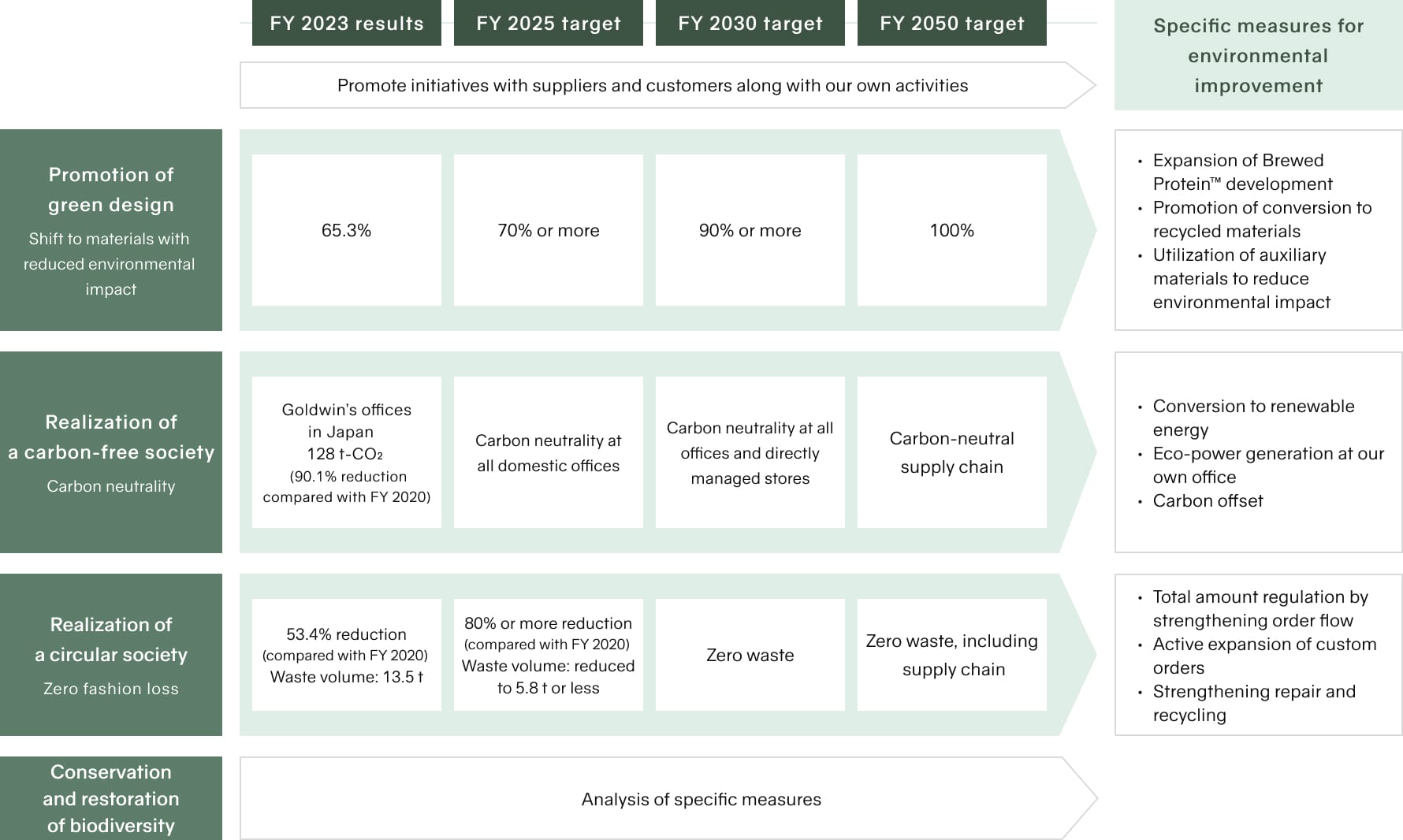
2. Greenhouse Gas Emission Reduction Targets and Results
(1) Reduction targets
We are striving to reach targets of carbon neutrality at all offices in Japan by 2025, and at all offices and directly managed stores by 2030, with the aim of being carbon neutral throughout our supply chain by 2050.
(2) Results
Please click on the link below for the latest information on our greenhouse gas emission reductions.