GOLDWIN cooperates developing gear for Hybrid Training System, a musculoskeletal training system for the International Space Station
Experiments scheduled for the flight mission in April 2014 (as of March 2014)
GOLDWIN Inc. (HQ: Shibuya, Tokyo/President: Akio Nishida/First Section of the Tokyo Stock Exchange: 8111) has developed fitting gear for Hybrid Training System (“HTS”), a musculoskeletal training system to be used at Kibo, the Japanese experiment module at the International Space Station.
The Japan Aerospace Exploration Agency (“JAXA”) will be conducting an experiment at the International Space Station to test HTS’s effectiveness as a countermeasure against muscular and skeletal atrophy in astronauts during their long-term stay in space.
The purpose of the experiment is to demonstrate the capability of HTS to maintain astronauts’ muscle strength in a weightless environment. As long-term space missions are becoming increasingly common, ensuring the health and well-being of the astronauts has been one of the most important challenges in recent years.
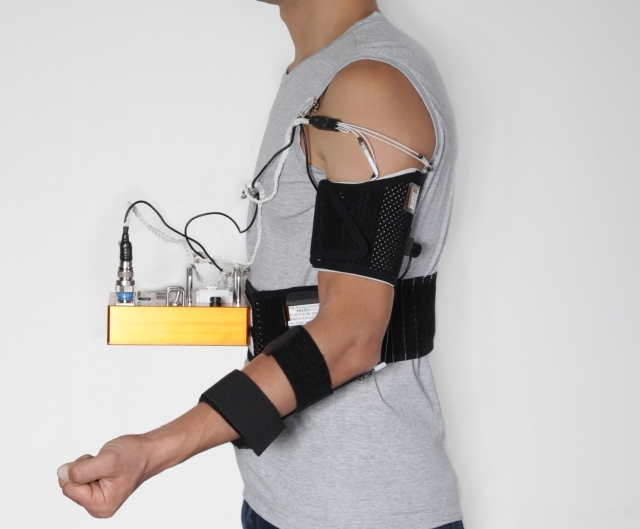
JAXA, Kurume University and Kyushu Institute of Technology jointly conducted the basic research and developed the specifications while Chiyoda Corporation was contracted by JAXA for system development. GOLDWIN was responsible for the design and development of the gear worn by astronauts when using HTS.
HTS consists of equipment and gear that take advantage of contraction produced by electrical simulation to strengthen the muscoskeletal system and the muscle strength measurement instrument that evaluates the result of training.
The gear developed by GOLDWIN can be easily configured by astronauts to position the electrodes without any special knowledge. It’s easy to put on without any assistance in a weightless environment and its electrodes can be secured with appropriate tightening force.
■ Featured product
Name: Hybrid Training System gear
Features:
Easy configuration of electrode positioning without expertise
Easy to put on without assistance under weightless condition
Specification development: JAXA, Kurume University, Kyushu Institute of Technology
Design/Production: Chiyoda Corporation